Fine-Tuning AI Models with Enterprise Data
Learn how to fine-tune AI models using data extracted from enterprise systems like Jira, ServiceNow, or Zendesk to create specialized support and knowledge agents.
Overview
Fine-tuning allows you to create specialized AI models that understand your organization's specific domain knowledge, terminology, and problem-solving approaches. By training models on historical support tickets, documentation, or domain-specific conversations, you can build AI assistants that provide more accurate, contextual responses.
This guide demonstrates how to build a complete fine-tuning pipeline using Tray workflows that:
- Extracts data from enterprise systems (Jira Service Desk, Zendesk, ServiceNow, etc.)
- Processes and transforms raw data into training format
- Uses AI to intelligently extract question-answer pairs
- Uploads training data to OpenAI's fine-tuning API
- Monitors fine-tuning job progress and notifies on completion
Use Cases
Fine-tuning is particularly valuable for:
- IT Support Agents: Train models on historical ITSM tickets to handle common technical issues
- Customer Support: Create support bots that understand your product-specific terminology and solutions
- Knowledge Management: Build agents that can answer questions using your organization's internal documentation style
- Domain Expertise: Develop specialized assistants for legal, medical, financial, or other regulated industries
- Multi-language Support: Fine-tune models to better handle company-specific translations and localized content
Architecture Overview
The solution consists of three interconnected workflows that orchestrate the entire fine-tuning process:
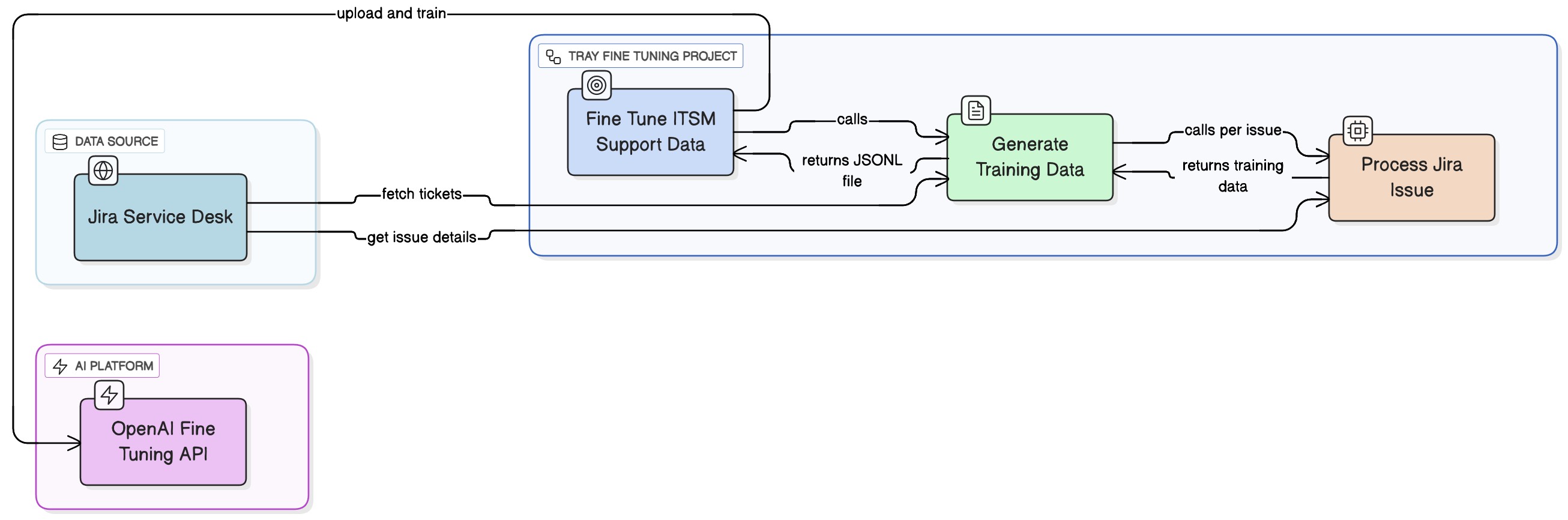
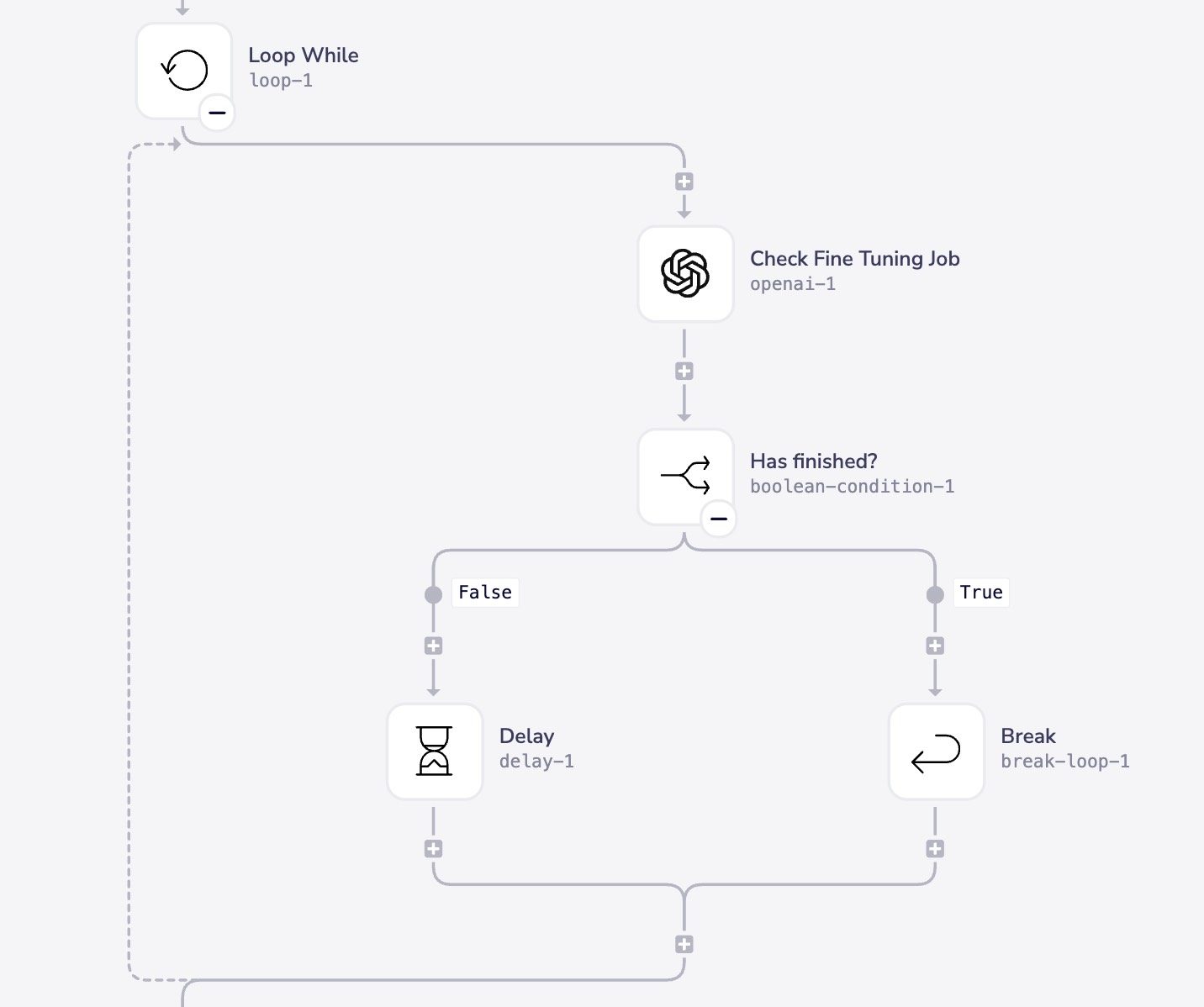
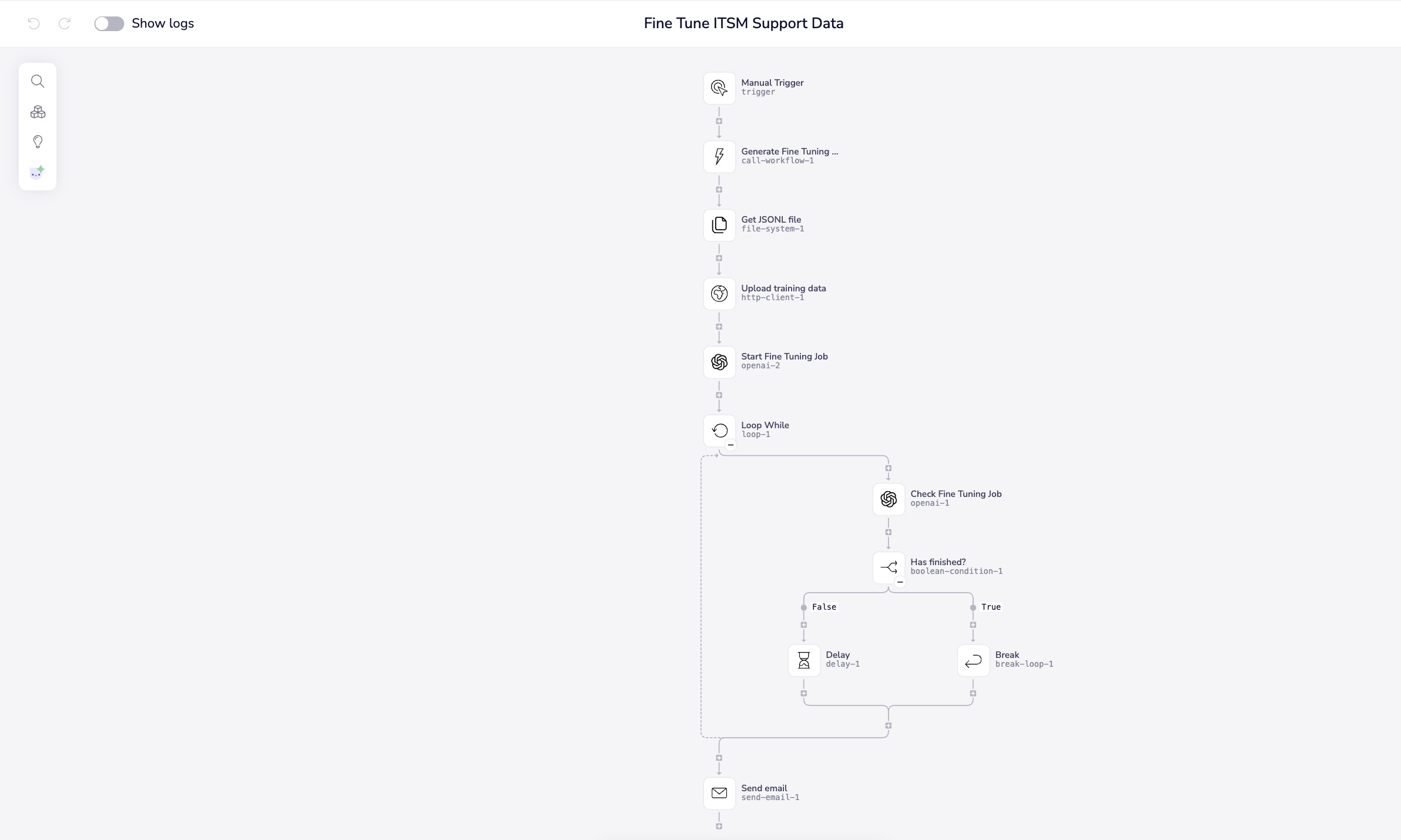
Workflow 1: Fine Tune ITSM Support Data (Main Orchestrator)
Purpose: End-to-end orchestration of the fine-tuning process
Key Steps:
- Manual trigger initiates the process
- Calls "Generate Training Data" workflow and receives the generated JSONL filename
- Retrieves the training file from Tray file storage
- Uploads file to OpenAI Files API
- Starts the fine-tuning job with target model
- Polls for job completion every 10 seconds
- Sends email notification when complete
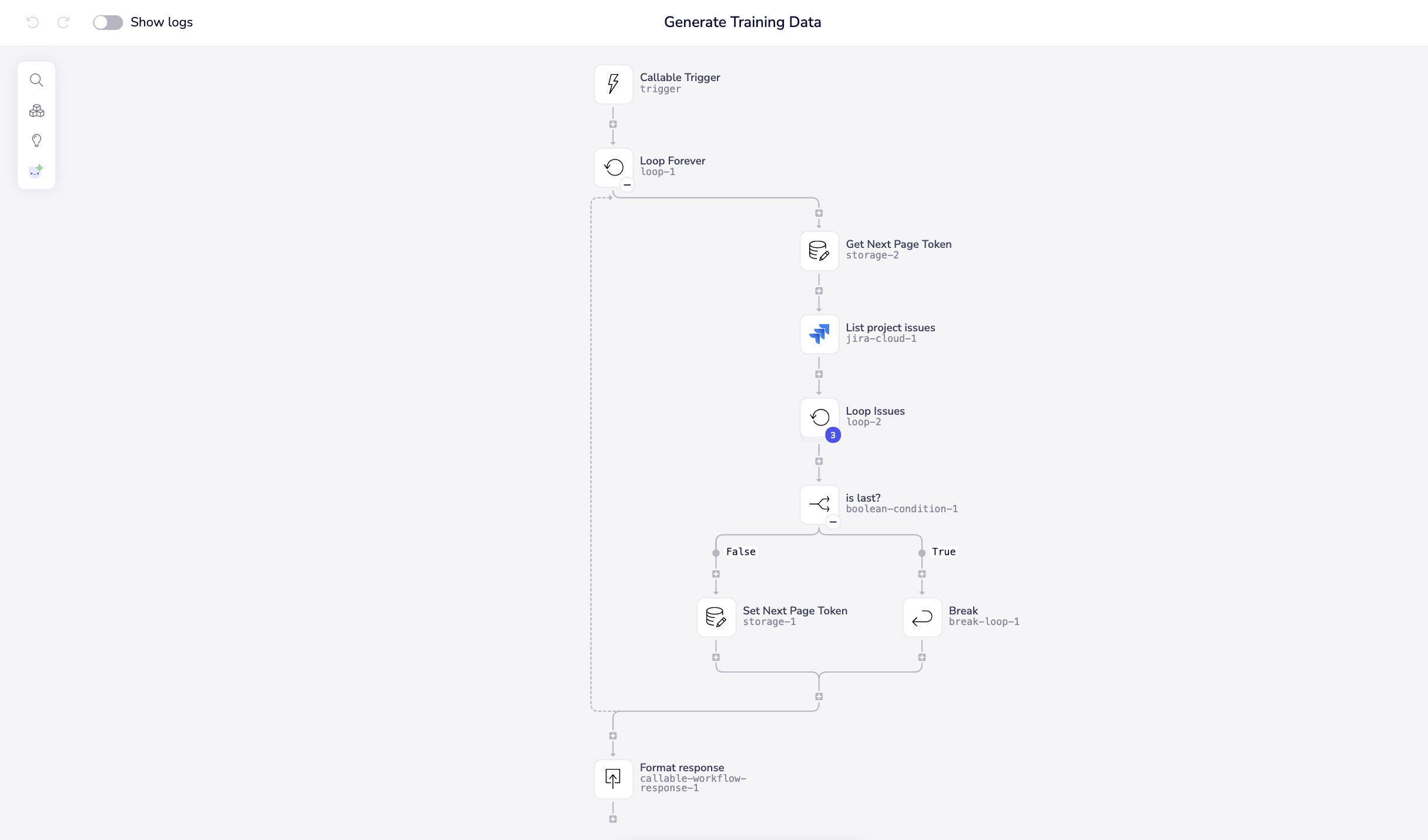
Workflow 2: Generate Training Data
Purpose: Extract and process source data into JSONL format
Key Steps:
- Callable trigger receives parameters from orchestrator
- Pagination loop handles Jira's paginated API responses
- For each issue, calls "Process Jira Issue" workflow
- Filters for resolved issues only (
solved === true) - Appends training examples to JSONL file
- Returns filename to orchestrator workflow
Workflow 3: Process Jira Issue
Purpose: Convert individual records into fine-tuning format using AI
Key Steps:
- Receives
issue_idparameter from caller - Fetches full issue details from Jira
- Extracts relevant fields (description, status, comments) using JSON transformer
- Sends to OpenAI with specialized extraction prompt
- Uses function calling to enforce structured JSON output
- Returns formatted training data and resolution status

Prerequisites
Before building the fine-tuning pipeline, ensure you have:
- OpenAI API Account: With fine-tuning access enabled (check your organization's tier)
- Data Source Authentication: Jira Cloud, Zendesk, ServiceNow, or other ITSM system configured in Tray
- Email Connector: Configured for completion notifications
- Tray File System Access: Available in all Tray accounts
- Minimum Training Data: At least 50-100 resolved tickets with clear Q&A conversations (OpenAI recommendation)
Fine-tuning costs vary based on model and training data size. Monitor your OpenAI usage dashboard during fine-tuning jobs. A typical job with 100 examples may cost between $10-50 depending on token count and model selection.
Current pricing (as of 2025): Check OpenAI's pricing page for gpt-4.1-2025-04-14 fine-tuning rates.
Understanding JSONL Format for Fine-Tuning
OpenAI's fine-tuning API requires training data in JSONL (JSON Lines) format, where each line is a complete JSON object representing one training example:
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "How do I reset my password?"}, {"role": "assistant", "content": "To reset your password, go to Settings > Security > Change Password. Enter your current password, then your new password twice to confirm."}]}
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Why is my API returning 401 errors?"}, {"role": "assistant", "content": "A 401 error indicates authentication failure. Check that your API key is valid and hasn't expired. You can generate a new key in the Admin console under API Access."}]}
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Can I export my data to CSV?"}, {"role": "assistant", "content": "Yes, use the Export feature under Reports. Select your date range and fields, then click Export to CSV. The file will be emailed to you within a few minutes."}]}
Key Format Requirements
- One training example per line: Each line must be a complete, valid JSON object
- Messages array: Contains exactly 2 messages for basic fine-tuning (user question + assistant response)
- Role specification:
"role"must be either"user"or"assistant" - Content field:
"content"contains the actual text - No trailing commas: Unlike JSON arrays, JSONL files don't have commas between lines
- Character escaping: Special characters must be properly escaped (use
<and>for angle brackets in email addresses)
Setting Up the Workflows
Step 1: Configure the Main Orchestration Workflow
Create a new workflow named "Fine Tune ITSM Support Data" with the following configuration:
Manual Trigger:
- Add a Manual Trigger to initiate the process on-demand
- Optionally add input parameters for:
project_key: Jira project to process (e.g., "SUPPORT")model: Target fine-tuning model (default:gpt-4.1-2025-04-14)notification_email: Email for completion notifications
Step 2: Start the Fine-Tuning Job
OpenAI Raw HTTP Connector:
- Method:
POST - Endpoint:
https://api.openai.com/v1/fine_tuning/jobs - Authentication: Use OpenAI authentication configured in Tray
- Body (JSON):
{
"training_file": "$.steps.http-client-1.body.id",
"model": "gpt-4.1-2025-04-14"
}
- Store the response job ID:
$.steps.openai-raw-1.body.id
You can add optional parameters like hyperparameters to customize the fine-tuning process. See OpenAI's fine-tuning documentation for available options.
Why polling? OpenAI fine-tuning jobs don't provide webhooks for completion notifications. Polling every 10 seconds is a balanced approach that provides timely notifications without hitting rate limits. For jobs with larger datasets (1000+ examples), consider increasing the polling interval to 30-60 seconds.
Step 3: Build the Data Generation Workflow
Create a workflow named "Generate Training Data" with a Callable Trigger:
Storage Connector - Initialize:
- Create variable:
next_page_token - Initial value:
null
Loop Forever Connector:
- Contains pagination logic to fetch all issues
Inside the loop:
-
Jira Get Issues (or equivalent for your system):
- Project: Map from trigger input
- Max results: 10 (batch size)
- Start at: Use
next_page_tokenfrom storage
-
Storage Connector - Set:
- Update
next_page_tokenwith response value
- Update
-
Boolean Condition:
- Check if
$.steps.jira-1.isLast === true
- Check if
-
Break Loop (conditional):
- Execute when no more pages remain
Step 4: Create the Issue Processing Workflow
Create a workflow named "Process Jira Issue" with a Callable Trigger that accepts issue_id:
Jira Get Issue Connector:
- Issue ID: Map from trigger
$.trigger.issue_id
JSON Transformer (JSONata):
- Expression:
{
"issue": $.fields.description,
"status": $.fields.status.name,
"comments": $.fields.comment.comments.body
}
- This extracts only the relevant fields needed for AI processing
Customizing for Different Data Sources
The solution architecture is designed to be adaptable to various enterprise systems:
Adapting for Zendesk
Replace the Jira-specific steps with Zendesk equivalents:
- Trigger: Use Zendesk's "Search Tickets" operation with status filter
solved - Pagination: Zendesk uses
next_pageURL in responses - Field Mapping: Adjust JSON transformer:
{
"issue": $.description,
"status": $.status,
"comments": $.comments[type='Comment'].body
}
Adapting for ServiceNow
- API Endpoint: Use ServiceNow's Table API for incidents
- Query: Filter for
incident_state=6(Resolved) andincident_state=7(Closed) - Field Mapping:
{
"issue": $.short_description & " " & $.description,
"status": $.incident_state,
"comments": $.comments
}
Adapting for Salesforce Cases
- SOQL Query:
SELECT Description, Status, Comments__c FROM Case WHERE Status = 'Closed' AND IsSolution = true - Field Mapping:
{
"issue": $.Description,
"status": $.Status,
"comments": $.Comments__c
}
Adapting for Custom Knowledge Bases
For documentation or knowledge base content:
- Source: Confluence, Notion, or custom documentation platforms
- Data Structure: Map article title to "user question" and article body to "assistant response"
- Filtering: Only include verified, published content
- System Prompt Modification: Adjust to focus on extracting key points rather than Q&A pairs
Monitoring and Validation
Understanding Fine-Tuning Job Statuses
OpenAI fine-tuning jobs progress through several states:
| Status | Description | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
validating_files | Initial validation of training data format | Wait |
queued | Job is queued for processing | Wait |
running | Fine-tuning is actively in progress | Wait |
succeeded | Job completed successfully | Use the fine-tuned model |
failed | Job encountered an error | Check error details, fix data, retry |
cancelled | Job was manually cancelled | Review and restart if needed |
Validating Training Data Quality
Before uploading to OpenAI, validate your training data:
Automated Validation:
- Minimum examples: At least 50 training examples (OpenAI minimum is 10, but 50+ yields better results)
- Format validation: Each line is valid JSON with required
messagesarray - Character encoding: All text is UTF-8 encoded
- Token count: Each example is under the model's context window (typically 4096-8192 tokens)
Manual Spot Checks:
- Questions are clear and self-contained
- Answers are complete and accurate
- No PII or sensitive data included
- Examples represent diverse scenarios
Adding Validation Steps to Your Workflow
Between data generation and OpenAI upload, add validation:
Script Connector (Validation):
const lines = inputs.file_content.split('\n').filter(l => l.trim());
const validation = {
total_lines: lines.length,
valid_json: 0,
invalid_json: 0,
errors: []
};
lines.forEach((line, idx) => {
try {
const obj = JSON.parse(line);
if (!obj.messages || obj.messages.length !== 2) {
validation.errors.push(`Line ${idx + 1}: Invalid messages array`);
} else {
validation.valid_json++;
}
} catch (e) {
validation.invalid_json++;
validation.errors.push(`Line ${idx + 1}: ${e.message}`);
}
});
return validation;
Best Practices
Data Quality Filtering
High-Quality Training Data Characteristics:
- Issues are fully resolved (status is "Closed" or "Resolved")
- Clear user question with complete assistant response
- Conversations are relevant to your target use case
- No duplicate or near-duplicate examples
- Balanced representation of issue types
- Technical accuracy verified
Optimal Training Data Volumes
OpenAI's recommendations for fine-tuning:
- Minimum: 10 examples (absolute minimum)
- Recommended: 50-100 examples for basic tasks
- Ideal: 200-500 examples for complex domains
- Maximum: No hard limit, but diminishing returns after 1000+ examples
Start small! Fine-tune with 100 carefully curated examples first. Evaluate the results, then incrementally add more training data if needed. Quality always trumps quantity.
System Prompt Engineering
The system prompt for AI extraction is critical:
Key Elements:
- Clear role definition ("You are a specialized assistant...")
- Specific task description (extract question, answer, status)
- Output format requirements (JSON structure via function calling)
- Quality guidelines (clarity, completeness, accuracy)
- Edge case handling (multiple issues, unclear resolution)
Iteration Strategy:
- Test with 5-10 sample tickets manually
- Review extracted Q&A pairs for quality
- Refine prompt based on common issues
- Re-test and iterate
- Only then run at scale
Handling Edge Cases
Multiple Issues in One Ticket:
- Use AI to identify the primary issue
- Create separate training examples if multiple distinct problems were solved
Unresolved or Partially Resolved Tickets:
- Filter out with
solved === false - Don't include in training data unless specifically training for escalation scenarios
PII and Sensitive Data:
- Add PII redaction step before AI extraction
- Use Merlin Guardian to automatically mask sensitive information (names, emails, SSNs, etc.)
- The masked data is safe for AI processing, and can be unmasked after extraction if needed
- Consider using synthetic or anonymized data for demonstration purposes
Non-English Content:
- Fine-tune separate models for each language
- Or use translation services before extraction (less ideal)
- Ensure your system prompt specifies the expected language
Troubleshooting
Common Issues and Solutions
Cost Optimization
Estimating Fine-Tuning Costs
OpenAI charges based on:
- Training tokens: Number of tokens in your training data × number of epochs
- Base model:
gpt-4.1-2025-04-14costs more thangpt-3.5-turbo - Usage fees: Fine-tuned model usage charges (input + output tokens)
Example calculation (using hypothetical rates):
- 100 training examples
- Average 200 tokens per example = 20,000 tokens total
- 3 epochs (default) = 60,000 training tokens
- At $0.008 per 1K tokens = ~$0.48 for training
Use the cheaper gpt-3.5-turbo for initial testing and prototyping. Only upgrade to gpt-4.1-2025-04-14 if you need the performance improvement. The cheaper model often performs well for domain-specific tasks.
Reducing Costs
Strategies:
- Curate data carefully: 100 high-quality examples > 500 mediocre ones
- Reduce epochs: Set
hyperparameters.n_epochsto 2 instead of default 3 - Filter aggressively: Only include truly resolved, clear examples
- Test with small batches: Start with 50 examples, evaluate, then scale
- Use base models when sufficient: Don't fine-tune if prompt engineering achieves good results
Next Steps
Once your fine-tuning job succeeds:
-
Test the Fine-Tuned Model:
- Use the model ID from the job response (e.g.,
ft:gpt-4.1-2025-04-14:your-org:custom-suffix:job-id) - Create a test workflow with OpenAI Chat Completion using your fine-tuned model
- Compare responses to the base model on sample questions
- Use the model ID from the job response (e.g.,
-
Deploy in Production:
- Integrate the fine-tuned model into your support chat workflows
- Build a callable workflow that uses the model for answering user questions
- Add fallback logic to use base model if fine-tuned model is unavailable
-
Iterate and Improve:
- Collect feedback on model responses
- Identify areas where the model underperforms
- Generate additional training data for weak areas
- Re-run fine-tuning with expanded dataset
-
Monitor Performance:
- Track model usage and costs in OpenAI dashboard
- Implement logging to capture model responses
- Set up alerting for unexpected behavior or costs
Additional Resources
- OpenAI Fine-Tuning Documentation
- Tray OpenAI Connector Documentation
- Building AI Knowledge Agents
- Vector Storage for RAG Pipelines
- Data Protection and Security
This documentation provides a comprehensive template for fine-tuning AI models with Tray. Adapt the workflows and configurations to match your specific data sources, organizational requirements, and use cases.