Workflow Tools
Expose Tray workflows as Composite Tools through your MCP server to execute complex multi-step business logic.
Workflow Tools expose complete Tray workflows as single tools that can be called via the MCP server. Each tool packages multi-step business logic, data transformations, validation, and error handling into one callable function.
What are Workflow Tools?
Workflow Tools (also called Composite Tools) are Tray workflows exposed through your MCP server. When a Workflow Tool is called, it executes the entire workflow with provided inputs and returns structured results.
Key benefits:
- Reduced context usage - One tool instead of multiple separate operations
- Built-in logic - Validation, error handling, and business rules embedded
- Lower hallucination risk - Controlled execution flow reduces AI decision points
- Governance - Human-in-the-loop approvals, audit logging, security controls
Why Use Workflow Tools?
Example: Sending a Slack Message
Without Workflow Tools, two separate operations are needed:
- Lookup user by name (returns multiple "Tom" results)
- Send message with user ID (caller must choose correct Tom)
This requires two LLM calls, uses more context, and risks sending to wrong person.
With a Workflow Tool, one Send Slack Message tool call handles everything:
- Accepts user name and message as inputs
- Workflow handles user lookup internally
- Workflow prompts for clarification if multiple matches
- Workflow sends to confirmed user
- Returns success confirmation
One LLM call, less context, correct execution guaranteed.
How MCP Workflow Tools Work
To expose a workflow as an MCP tool, your workflow must be built with two specific components:
Agent Tool Trigger
The Agent Tool Trigger is the entry point at the start of your workflow that receives requests through the MCP server. Configure this trigger to await the workflow execution. When your workflow tool is called, this trigger:
- Receives the tool call with input parameters
- Makes the workflow executable by MCP clients
- Passes inputs to your workflow logic
Trigger Reply
The Trigger Reply connector sends the workflow's response back to the caller. This connector:
- Returns structured output to the caller
- Completes the tool execution cycle
- Provides results to continue the task
Both the Agent Tool Trigger and Trigger Reply connectors are required for a workflow to function as an MCP tool. Without these connectors, your workflow cannot be called or return responses through MCP.
You do not need to create an Agent project to use Workflow Tools. Any standard Tray workflow built with the Agent Tool Trigger and Trigger Reply can be exposed as an MCP tool.
Basic Flow:
- Workflow tool is called through MCP server
- Agent Tool Trigger receives the call and inputs
- Workflow executes business logic
- Trigger Reply returns results to caller
- Caller continues with received workflow output
Making Workflows Available as Tools
Step 1: Build your workflow
Create a workflow with the required components:
- Add an Agent Tool Trigger as the workflow start point (configure it to await)
- Define input parameters in the trigger configuration
- Build your workflow logic (connectors, data transformation, etc.)
- Add a Trigger Reply connector to send the response back to the caller
- Optionally add additional steps after the Trigger Reply (logging, cleanup, etc.)
- Enable the workflow
Step 2: Expose the workflow through MCP
- Navigate to Workspace Settings → Agent Gateway → MCP Server
- Click the Workflow tools tab
- Click Add workflow tool to open the selection dialog
- Only workflows with Agent Tool Trigger and Trigger Reply will appear in the list
- Select the workflows you want to expose as MCP tools
- Click Add or Save
Once added, each workflow becomes an MCP tool with:
- Tool name: Derived from workflow name
- Tool description: From workflow description
- Input schema: Defined in Agent Tool Trigger
- Output schema: Defined in Trigger Reply
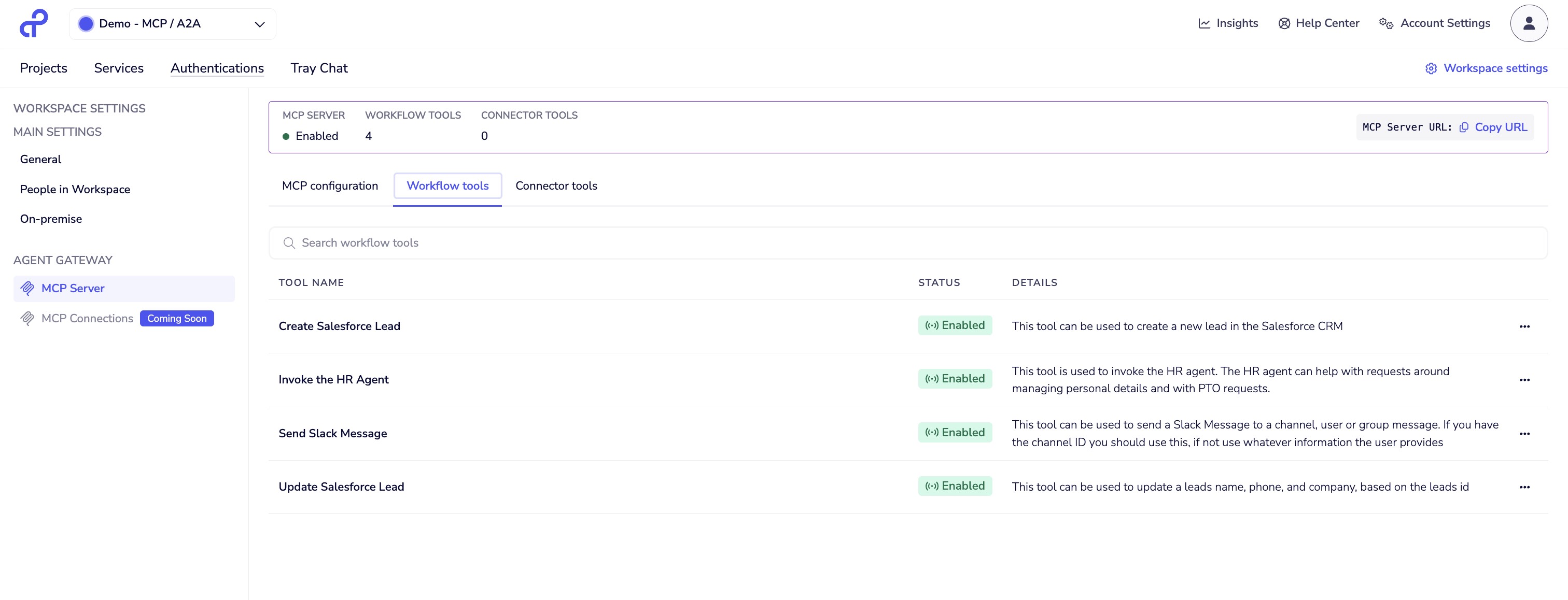
If your workflow doesn't appear in the selection list, verify it includes both the Agent Tool Trigger and Trigger Reply connector, and that the workflow is enabled.
Designing Effective Tools
Input Design
Define clear parameters with validation in the workflow:
Create Salesforce Lead inputs:
- Lead name (required)
- Company (required)
- Phone (optional)
- Email (optional)
Output Design
Return structured, actionable data:
{
"success": true,
"lead_id": "00Q5e00000ABC123",
"lead_url": "https://company.salesforce.com/00Q5e00000ABC123",
"message": "Lead created successfully for John Doe at Acme Corp"
}
Tool Descriptions
Write clear descriptions explaining what, when, and how:
✅ Good: "Sends Slack message to specified channel, user, or group. Uses channel ID if available, otherwise looks up by name. Prompts for clarification if multiple matches found."
❌ Avoid: "Sends messages to Slack."
Common Patterns
Data Lookup with Validation
- Search records by criteria
- Validate results (single/multiple/no match)
- Handle edge cases (expired records, permissions)
- Use case: Customer lookup before creating support ticket
Multi-System Orchestration
- Retrieve data from System A
- Transform per business rules
- Update System B
- Notify via System C
- Use case: Invoice processing across ERP and accounting
Human-in-the-Loop Approval
- Receive request
- Validate parameters
- Request approval
- Execute if approved
- Use case: High-value purchase orders
Read-Only Aggregation
- Query multiple systems
- Aggregate and calculate
- Return formatted summary
- Use case: Customer 360 view
Best Practices
Keep tools focused:
- One business function per tool
- Avoid generic "do everything" tools
- ✅ Good: "Create Salesforce Lead", "Update Salesforce Lead"
- ❌ Avoid: "Manage Salesforce"
Build robust error handling:
- Catch API errors gracefully
- Return clear error messages
- Log for debugging
- Implement retry logic where appropriate
Test thoroughly:
- Expected inputs
- Invalid/missing inputs
- Error conditions
- Edge cases
- Verify outputs are interpretable
Document clearly:
- Workflow documentation becomes tool description
- Document parameters and formats
- Include example use cases
- Note limitations and prerequisites
Managing Tools
Enabling/Disabling:
- View all exposed workflows in Workflow tools tab
- Toggle individual tools on/off
- Status indicator shows enabled/disabled state
Updating:
- Workflow changes reflect immediately
- No MCP server reconfiguration needed
- Schema updates are reflected automatically
Removing:
- Click options menu (•••) next to tool
- Select remove/disable
- Tools become immediately unavailable
Troubleshooting
Tool not found:
- Verify workflow is enabled
- Check MCP server is enabled
- Ensure tool is enabled in Workflow tools tab
- Restart AI client
Execution fails:
- Check workflow logs
- Verify input format matches schema
- Ensure workflow has necessary permissions
- Test manual execution
Tool is used incorrectly:
- Improve tool description clarity
- Add input validation in workflow
- Consider splitting into more focused tools
Next Steps
- Connector Tools - Expose individual connector operations
- MCP Server Configuration - Configure server settings
- Connecting MCP Clients - Set up AI clients