Environment variables
There is a list of $.env variables that - at any point in your workflow - can be used to access basic info about the workflow/solution environment
There is a list of Tray environment variables (prefixed with $.env) that - at any point in your workflow - can be used to access basic info about the workflow/solution environment. These are:
$.env.execution_uuid
$.env.execution_start_time
$.env.execution_log_url
$.env.organization_uuid
$.env.project_id
$.env.solution_id
$.env.solution_instance_id
$.env.source_workflow_uuid
$.env.workflow_uuid
$.env.workflow_title
$.env.workspace_id
Tray's $.env environment variables are fixed and it is not possible to create custom $.env variables
An alternative approach may be to use project config variables which are entirely customizable and can be accessed using the $.config jsonpath
The execution uuid
The $.env.execution_uuid environment variable is potentially of key importance in managing statuses and errors.
It is the id which is generated every time a workflow is run.
It could be linked to an external execution id (which may have been pulled in from a webhook) - both of which could be stored in Data Storage and retrieved later in the workflow or stored at account level and retrieved in any child workflows which are called.
The workflow uuid
The $.env.workflow_uuid environment variable is basically the uuid found in your workflow url:
 An example of using
An example of using $.env.workflow_uuid can be found in our documentation on workflow threads
In this case it is used as a suffix for an account-level data storage variable, to identify that the variable is connected to that workflow
Callable workflow trigger variables
Callable workflows have the following environment variables available from their trigger output:
$.steps.trigger.#calling_workflow
$.steps.trigger.#calling_execution
$.steps.trigger.#calling_execution_log_url
The $.steps.trigger.#calling_workflow environment variable can be used to obtain the uuid of the calling workflow.
Again, this is used in our documentation on workflow threads - to make sure the calling workflow accesses the account-level data storage list that was created by the calling workflow.
Embedded environment variables
There is a further list of environment variables that can be used to access basic info about the solution environment in your Embedded integrations. These are:
$.env.execution_uuid
$.env.execution_start_time
$.env.user_id
$.env.external_user_id
$.env.execution_log_url
$.env.workflow_uuid
$.env.workflow_title
$.env.solution_id
$.env.solution_instance_id
$.env.source_workflow_uuid
For example, if you have a step which produces the following error output:
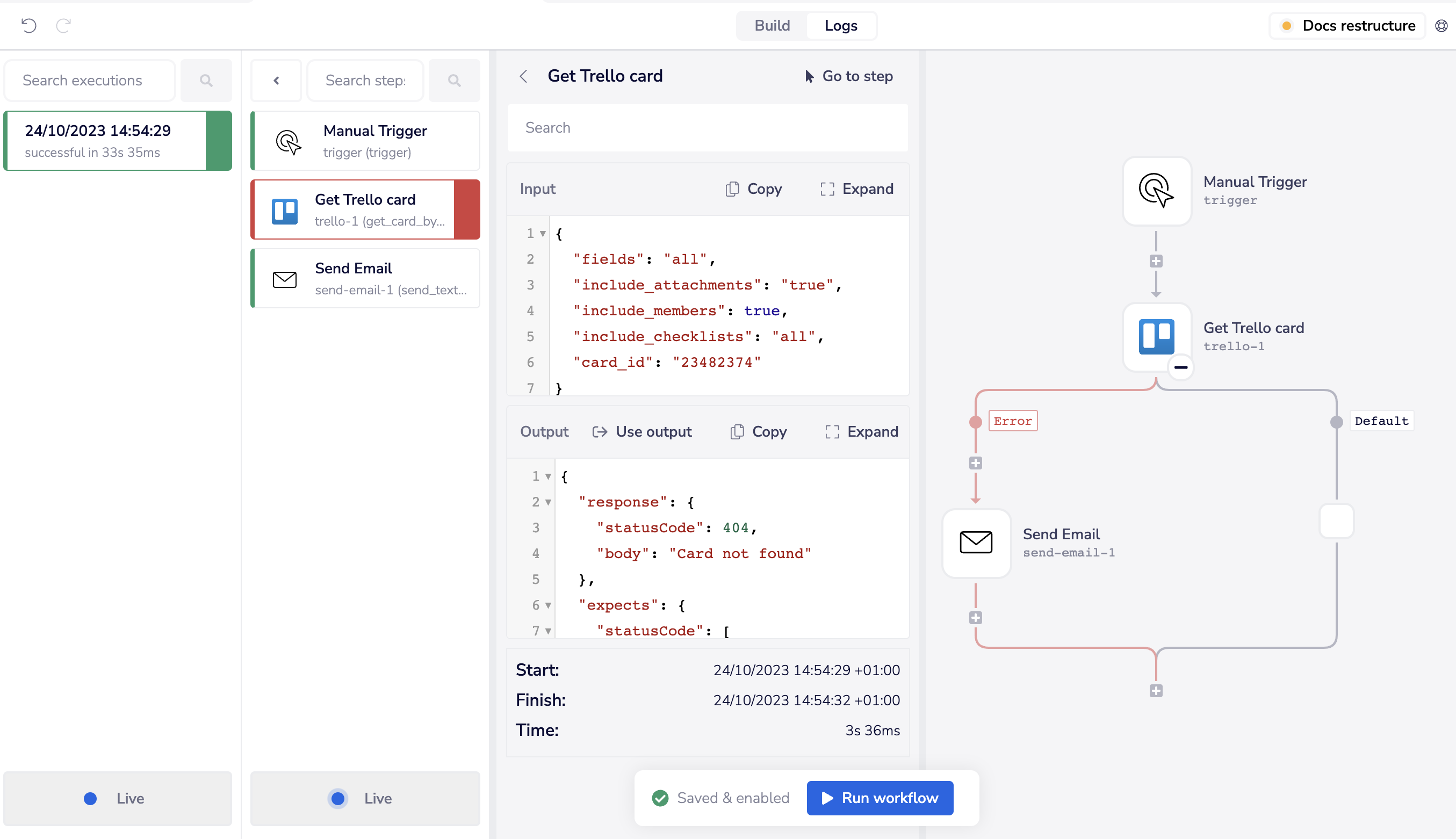 You could use the following:
You could use the following:
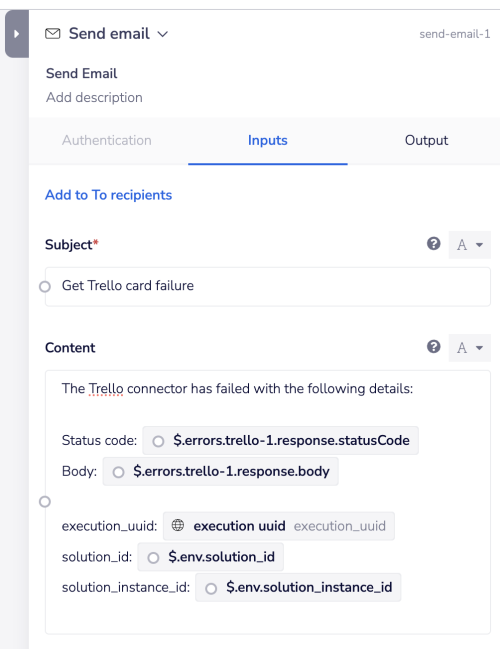 To format a message which would produce the following:
To format a message which would produce the following:

Environment variables and fallback values
When building Embedded Solutions, you should set fallback values when using environment variables.
For example, $.env.solution_instance_id is only available in the solution instance context and you will get errors while testing the master workflow as the jsonpath isn't yet available.